Late in 2014, the World Health Organisation issued guidelines for the management of several HIV-related skin and oral diseases, in low resource settings. Led by Prof Rod Hay (International Foundation for Dermatology, London) and Toby Maurer (UCSF School of Medicine, San Francisco), all the clinical trial evidence for diagnosis and management was scrutinized using the Grade criteria, and recommendations made.
Professor Denning GAFFI’s president stated “GAFFI welcomes the WHO first guidelines on how to care for HIV patients with skin and mouth fungal infections. These infections are incredibly common in AIDS all over the world, and cause real discomfort and leave many patients ostracised by their communities. Hopefully the WHO will also approve the inclusion of itraconazole on the EssentIal Medicines List as well, opening up avenues of external funding for the poorest countries and communities”.
The conditions the fungal conditions include: oral candidiasis, seborrhoeic, dermatitis, eosinophilic folliculitis and tinea infections and the non-fungal conditions Kaposi sarcoma, popular pruritic eruption, herpes zoster, scabies, mollucscum contagiosum, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
The treatment recommendations can be summarized:
Oral candidiasis
- adults: Fluconazole 100-150mg/d for 7 days, or topical alternative
- children: Fluconazole 3mg/Kg for 7-14 days, or topical therapy with clotimazole or nystatin
· Seborrhoeic, dermatitis
- mild: topical ketoconazole 2% 2-3 times weekly for 4 weeks, then weekly
- severe: topical antifungals (ie ketoconazole 2%) and corticosteroid ointment
· Eosinophilic folliculitis:
- Oral antihistamine first. If no response add topical corticosteroid (ie betamethasone). If no response add itraconazole (200mg daily). If no response add permethrin 5% cream (above the waist).
· Tinea infections
- localized: topical terbinafine 1% cream/gel for 2 weeks or miconazole topically for 4 weeks.
- extensive or hair/nail invovement: oral griseofulvin or itraconazole 200mg daily, duration dependent on infection site.
(Separate recommendations are made with pregnancy).
The guidelines are here: and available online through the Maternal and Child Health division of WHO
Images:
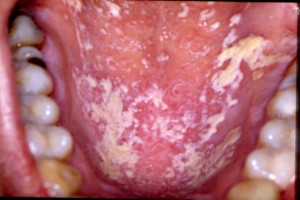
Oral candidiasis

Seborrheic dermatitis