On World Aspergillosis Day, GAFFI highlights the significant strides forward in the diagnosis of all forms of aspergillosis over the last few years.
Major advances include:
- Introduction of lateral flow assays for Aspergillus antigen
- Introduction of lateral flow assay for Aspergillus antibody
- Determination of cut-offs for Aspergillus antibody for multiple tests and countries
- The increased yield of high volume culture of respiratory samples
- Extended use of susceptibility testing of Aspergillus – identifying resistance
- Understanding of the increased sensitivity of both Aspergillus PCR and culture of respiratory samples
- Improved proteomics databases for rapid species identification of Aspergillus from culture.
The dramatic problems with both aspergillosis and mucormycosis in COVID patients have highlighted the need for increased vigilance and diagnostic speed. The two potentially fatal fungal infections have a similar clinical presentation, but can be distinguished by laboratory testing in >90% of cases.
These advances and their interpretation were recently summarised in a review paper by Professor David Denning in the International Journal of Lung Disease and Tuberculosis. Antigen, antibody and culture are all WHO-listed Essential Diagnostics.
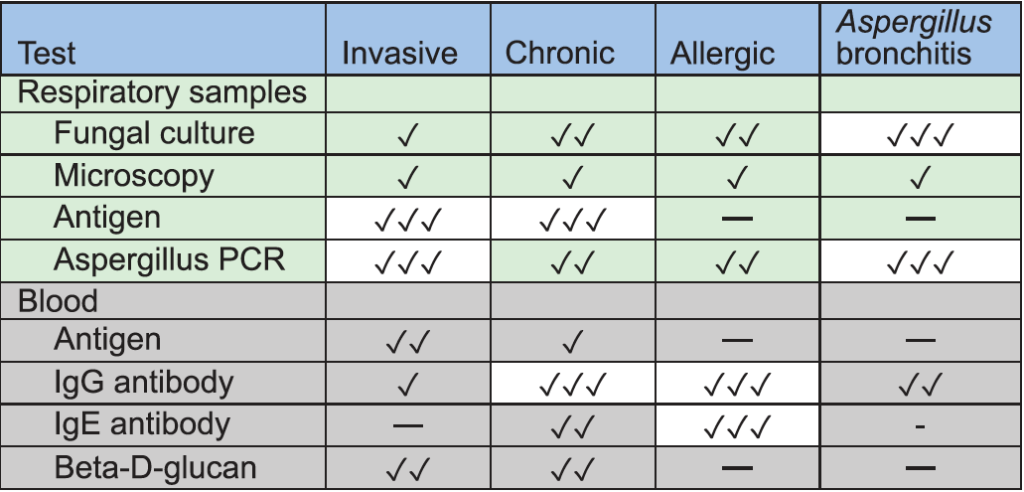
✓ = up to 35% sensitive, ✓✓ = 35-75% sensitive, ✓✓✓ = better than 75% sensitive.
Major challenges remaining are primarily related to access to these diagnostics and clinician awareness of patients at risk. GAFFI is working with multiple partners to improve understanding of these diseases. Many resources are available online.


